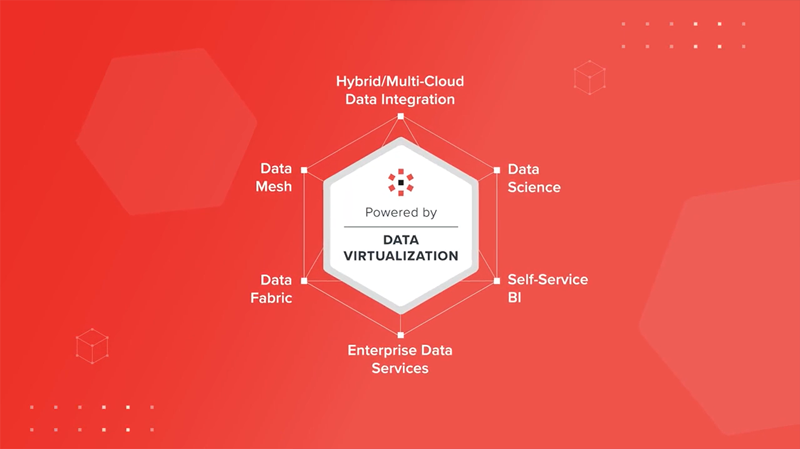
As demand for data grows, organizations need to shorten time-to-value by accelerating data engineering efforts. Most current approaches are too slow and costly, they cause reinvention, and they can lead to inconsistent data. Data virtualization, in contrast, provides an agile approach to creating data products. With data virtualization, data products can be governed in one place and provisioned to consumers without replication. Data virtualization is an excellent foundation for modern distributed data architecture and use cases.
Data Architects
Data virtualization adds data integration flexibility so data architects can successfully evolve their data strategies and architectures to take full advantage of the latest data technologies and innovations.
Data Engineers
Easy to learn and highly productive to use, data virtualization enables data engineers to deliver more data views, faster, so they can realize more business value, sooner.
Data Scientists and Analysts
Data virtualization provides data scientists and analysts with instant access to all the data they want, the way they want it.
Analytics Leaders
Data virtualization simplifies and accelerates access to the data needed to fuel analytics and applications.
CIOs and CTOs
Data virtualization’s agile integration approach enables CIOs and CTOs to respond more quickly to ever-changing business needs and do so for less of an investment.
Data Stewards
Data virtualization helps data stewards implement and enforce enterprise data models and standards to provide consistent, secure, and governed data.