Have a question?
Free Trial
Experience the full benefits of Denodo Enterprise Plus with Agora, our fully managed cloud service.
START FREE TRIALHave a question?
(+1) 650 566 8833

Cloud computing is the delivery of computing services—including servers, storage, databases, networking, software, and analytics—over the Internet (“the cloud”). It enables organizations and individuals to access and manage data and applications without needing on-premises infrastructure.
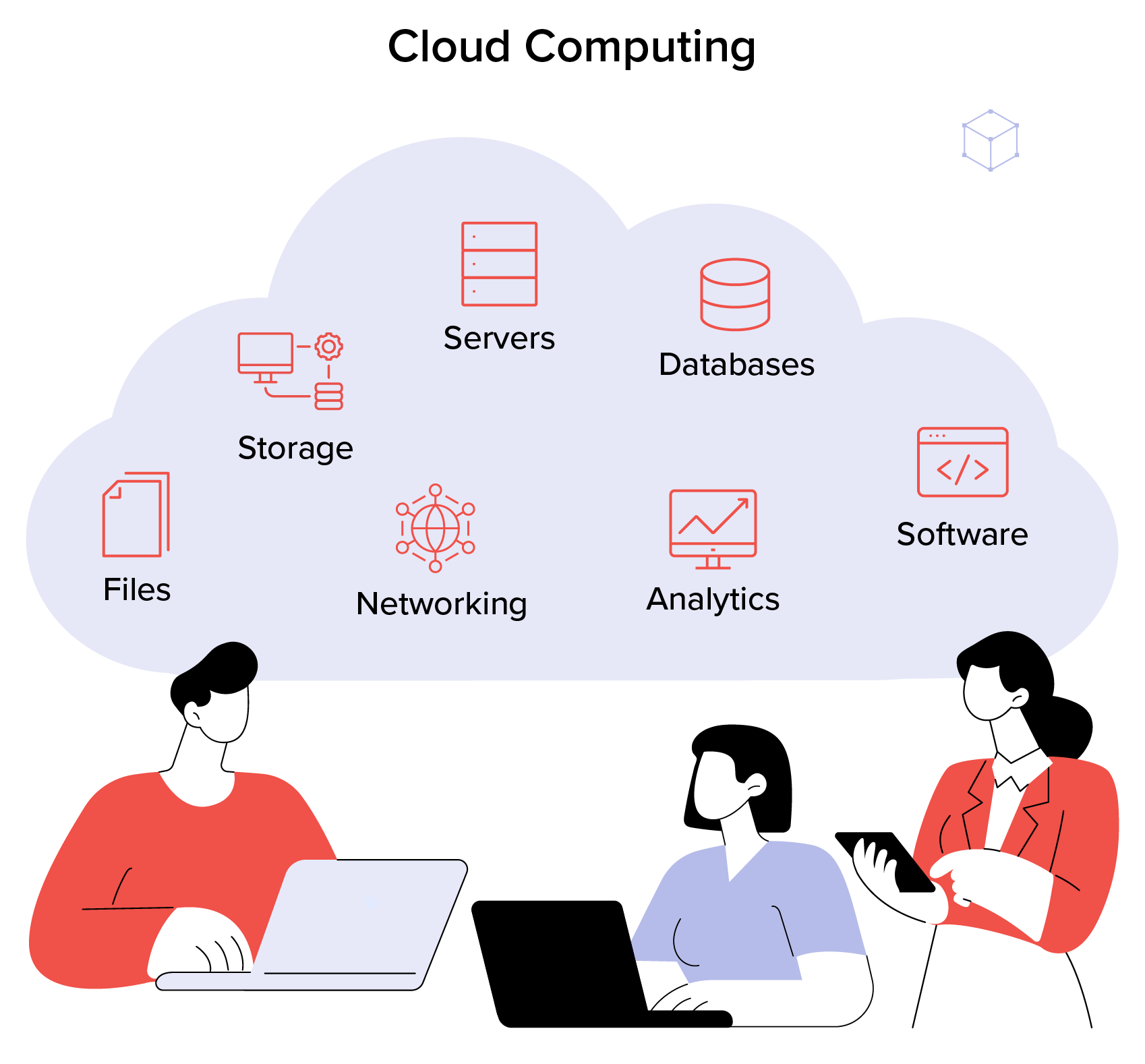
Cloud computing offers scalable, cost-effective, and flexible data solutions. With cloud computing, organizations can access computing resources on demand, enhance collaboration, and reduce IT maintenance costs. It enables remote work, disaster recovery, and efficient data management.
Cloud computing is a broad category of technology solutions, but many will have some, if not all, of the following characteristics:
Individual cloud computing systems fall under these broad categories:
Cloud computing systems meet a variety of needs for a variety of different users, from technical users to consumer users. Depending on their focus, cloud systems are categorized in a number of different “as a service” groups:
Cloud computing is as diverse as computing itself. As such, cloud computing applications are many and various. They include:
Cloud computing saw widespread adoption, due to its many benefits:
However, cloud computing does present a number of challenges, including:
The Denodo Platform simplifies data access, accelerates data delivery, and enables trusted, AI-powered insights across both on-premises systems and the cloud, and it provides specialized support for the cloud:
The Denodo Platform can be flexibly deployed both on-premises and in the cloud.
Denodo has partnered with the major cloud providers and has implemented the Denodo Platform in a variety of different hybrid and cloud ecosystems. Here are two examples:
Though cloud computing has been evolving for a number of years, it is still incorporating new discoveries and innovations. In the future of cloud computing, keep an eye out for the following developments:
Experience the full benefits of Denodo Enterprise Plus with Agora, our fully managed cloud service.
START FREE TRIAL